As a supplier of anhydrides, I've witnessed firsthand the widespread use of these chemical compounds in various industries. Anhydrides are versatile chemicals with applications in plastics, resins, pharmaceuticals, and more. However, it's crucial to understand that along with their utility, anhydrides pose several hazards that demand careful handling and management. In this blog, I'll delve into the potential dangers associated with anhydrides and why safety should always be a top priority.
Chemical Burns and Skin Irritation
One of the most immediate hazards of anhydrides is their ability to cause severe chemical burns and skin irritation. Anhydrides are highly reactive compounds that can react with water in the skin, releasing heat and forming corrosive acids. When anhydrides come into contact with the skin, they can quickly break down the skin's protective barrier, leading to redness, swelling, pain, and in severe cases, blistering and ulceration.
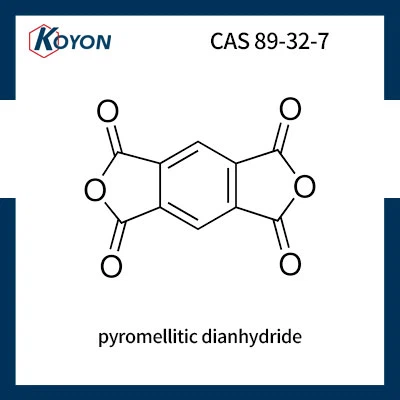
For example, Maleic Anhydride is a common anhydride used in the production of unsaturated polyester resins. Exposure to maleic anhydride can cause immediate skin irritation, and prolonged or repeated contact can lead to sensitization, where the skin becomes increasingly sensitive to the chemical. Similarly, Pyromellitic Dianhydride and Trimellitic Anhydride, which are used in the manufacture of high-performance polymers and coatings, can also cause significant skin damage if proper precautions are not taken.
To prevent skin exposure, it's essential to wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, aprons, and protective clothing, when handling anhydrides. In addition, workers should thoroughly wash their hands and any exposed skin with soap and water after handling these chemicals.
Respiratory Hazards
Inhalation of anhydride dusts, mists, or vapors can pose serious respiratory hazards. When anhydrides are heated, processed, or handled in a way that generates airborne particles, they can be inhaled into the lungs, where they can cause irritation, inflammation, and damage to the respiratory tract.
Exposure to anhydrides can lead to symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness. In severe cases, it can cause chemical pneumonitis, a condition characterized by inflammation and fluid accumulation in the lungs. Long-term exposure to anhydrides has also been associated with an increased risk of developing chronic respiratory diseases, such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
To minimize the risk of inhalation exposure, it's important to use proper ventilation systems in areas where anhydrides are handled or processed. Local exhaust ventilation can effectively capture and remove airborne particles at the source, while general ventilation can help dilute and remove any remaining contaminants from the air. Workers should also wear appropriate respiratory protection, such as respirators, when working in environments where anhydride exposure is likely.
Eye Irritation and Damage
Anhydrides can cause severe eye irritation and damage if they come into contact with the eyes. Like the skin, the eyes are sensitive to the corrosive effects of anhydrides, and exposure can lead to redness, pain, tearing, and blurred vision. In severe cases, it can cause permanent damage to the cornea and other structures of the eye, leading to vision loss.
To prevent eye exposure, workers should wear safety goggles or face shields when handling anhydrides. In the event of eye contact, it's important to immediately flush the eyes with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes and seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Environmental Hazards
In addition to the health hazards associated with anhydrides, they can also have a significant impact on the environment. Anhydrides are often released into the environment during their production, use, and disposal, and they can contaminate soil, water, and air.
When anhydrides are released into water bodies, they can react with water to form acidic compounds, which can lower the pH of the water and harm aquatic life. Anhydrides can also persist in the environment for long periods of time, and they can bioaccumulate in the tissues of living organisms, posing a risk to wildlife and human health.
To minimize the environmental impact of anhydrides, it's important to follow proper waste management practices. Anhydrides should be stored, handled, and disposed of in accordance with local regulations and guidelines. In addition, industries should strive to reduce their use of anhydrides and explore alternative, more environmentally friendly chemicals and processes.
Fire and Explosion Hazards
Some anhydrides are flammable or combustible, and they can pose a fire and explosion hazard if not handled properly. Anhydrides can react with oxidizing agents, such as strong acids and peroxides, to produce heat and potentially explosive mixtures. In addition, some anhydrides can decompose when heated or exposed to certain conditions, releasing flammable gases.
To prevent fire and explosion hazards, it's important to store anhydrides in a cool, dry, well-ventilated area away from sources of heat, ignition, and oxidizing agents. Workers should also follow proper handling procedures when working with anhydrides, such as avoiding spills and ensuring that containers are properly sealed.
Conclusion
As a supplier of anhydrides, I understand the importance of balancing the benefits of these chemicals with the need to ensure the safety of workers, the public, and the environment. While anhydrides have many valuable applications in various industries, they also pose significant hazards that must be carefully managed.
By understanding the potential hazards associated with anhydrides and implementing appropriate safety measures, we can minimize the risk of exposure and protect the health and well-being of everyone involved. If you're considering using anhydrides in your business, I encourage you to contact me to discuss your specific needs and to learn more about the safety precautions that should be taken. Together, we can ensure that anhydrides are used safely and responsibly.

References
- "Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) - Chemical Hazards and Toxic Substances." OSHA.gov.
- "National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) - Chemical Hazards." NIOSH.gov.
- "Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) - Chemical Safety and Pollution Prevention." EPA.gov.
